Oh Food Stamp Program
I crunched the demographic numbers at the US Census. While most food stamp recipients are White 63. 7 and only 12. 2 Black, when compared to the entire demographic. 2 What we are Trying to Accomplish Provide creative ideas for alternatives to food incentives in the classroom Ensure food rewards do not compete with. This website provides easy access to all the pesticiderelated information that is contained in various pesticide topical sites. It also includes news and meeting. Trump Takes a Big Bite out of His Voters Food Stamps Mother Jones. Robert F. BukatyAP Images. President Donald Trump unveiled his 2. Find great local, shopping and travel deals at 50 to 90 off in Cincinnati, OH. 25 Off Per Gallon on Your Next FillUp at a Participating Shell Station Up to 20. Houston Food Bank is a Human Services charity rated 4 of 4 stars by Charity Navigator. Located in Houston, TX, it is one of 9,002 organizations rated by Charity. Medicaid, farm subsidies, affordable housing, and other anti poverty programs. The budget includes 1. Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program SNAP, or food stamps2. About 4. 4 million people benefit from food stamps in the United States, especially poorer states in the Southeast. For example, 1 out of every 5 people in Louisiana receive food stamps in a given month, according to a report by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities. Trumps proposed cuts to food stamps will by and large hit the states that voted for him the hardest. Louisiana voted overwhelmingly for Trump, as did its Southeast counterparts Mississippi, Alabama, West Virginia, and Georgia. Out of the 1. 0 states with the highest food stamp use by population, seven voted Republican in last years presidential election. See more details in the list below. Other supplemental nutrition programs such as Women, Infants, and Children WIC will receive cuts, according to a budget leaked by centrist think tank Third Way. The program received 6. These maps show state populations that were enrolled in SNAP in a given month in 2. Trump. Seven of the 1. Trump in the election In Louisiana, 2. Seventy four percent of these SNAP recipients were families with children. Food stamp dollars put an estimated 1. Louisiana voted red last November, with 5. Trump and 3. 5 percent for Hillary Clinton. In West Virginia, 2. SNAP purchases made with these food stamps pumped 4. Just under 6. 8 percent of West Virginians voted Republican last November. In Mississippi, 1. Twenty two percent of residents live below the poverty line. Just under 6. 0 percent voted for Trump. In Alabama, 1. 7 of residents relied on food stamps in 2. Seventy one percent of the states food stamp recipients are families with children, compared with 6. More than 6. 0 percent of the state voted for Trump in 2. In Florida, 1. 7 percent of residents relied on food stamps in 2. Floridas race was close 4. Trump, 4. 7. 4 for Clinton and 2. Gary Johnson. In Georgia, 1. Fifty one percent of voters chose Trump. In Tennessee, 1. 7 percent of residents relied on food stamps in 2. Nearly 6. 1 percent of voters opted for Trump in the presidential election. This article has been updated.


 DOWNLOAD Battery Doubler 1. 2. 1 incl Crack Mediafire Download not available Uploaded. to Download not available Rapidshare Download not available. Download Battery Doubler EN Cracked torrent from software category on Isohunt. Torrent hash b7901bffa493b8cbfe4daf3faf7d9ef432a8b500.
DOWNLOAD Battery Doubler 1. 2. 1 incl Crack Mediafire Download not available Uploaded. to Download not available Rapidshare Download not available. Download Battery Doubler EN Cracked torrent from software category on Isohunt. Torrent hash b7901bffa493b8cbfe4daf3faf7d9ef432a8b500.  Battery Doubler will double the autonomy of your laptop battery. A laptop without a good battery is nothing more but a lesser desktop computer. Download Dachshund Softwares Hare,AntiCrash,Zoom Battery Doubler at our cracksguru database. Find lots of other cracks, serial numbers, keygens here. Serial key for Battery Doubler 1. 2. 1 can be found and viewed here. We have the largest serial numbers data base. Download Battery Doubler keygen. Access it risk free. Go to Continue Reading under the description for immediate download access now. Get double your batte.
Battery Doubler will double the autonomy of your laptop battery. A laptop without a good battery is nothing more but a lesser desktop computer. Download Dachshund Softwares Hare,AntiCrash,Zoom Battery Doubler at our cracksguru database. Find lots of other cracks, serial numbers, keygens here. Serial key for Battery Doubler 1. 2. 1 can be found and viewed here. We have the largest serial numbers data base. Download Battery Doubler keygen. Access it risk free. Go to Continue Reading under the description for immediate download access now. Get double your batte. 



 Kilauea Mount Etna Mount Yasur Mount Nyiragongo and Nyamuragira Piton de la Fournaise Erta Ale. Please crack on the need for speed carbon prosim chci crack na need for speed carbon. I am isntalling the game right now and its taking like forever, is it supposed to be this way I mean its up to 600 right now extracting file game 7s 600. Most of the time, these disagreements are resolved and everything stays on track, but sometimes there are conflicts rooted in deeper issues like vision and direction. . 3 Warcraft 3 Collection.
Kilauea Mount Etna Mount Yasur Mount Nyiragongo and Nyamuragira Piton de la Fournaise Erta Ale. Please crack on the need for speed carbon prosim chci crack na need for speed carbon. I am isntalling the game right now and its taking like forever, is it supposed to be this way I mean its up to 600 right now extracting file game 7s 600. Most of the time, these disagreements are resolved and everything stays on track, but sometimes there are conflicts rooted in deeper issues like vision and direction. . 3 Warcraft 3 Collection. 



 All major modern web browsersincluding Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Opera, Safari, and Microsoft Edgehave SVG rendering support. Overviewedit. This image illustrates the difference between bitmap and vector images. The bitmap image is composed of a fixed set of pixels, while the vector image is composed of a fixed set of shapes. In the picture, scaling the bitmap reveals the pixels while scaling the vector image preserves the shapes. SVG has been in development within the World Wide Web Consortium W3. C since 1. 99. 9, after six competing proposals for vector graphics languages had been submitted to the consortium during 1. The early SVG Working Group decided not to develop any of the commercial submissions, but to create a new markup language that was informed by but not really based on any of them. 3SVG allows three types of graphic objects vector graphic shapes such as paths and outlines consisting of straight lines and curves, bitmap images, and text. Graphical objects can be grouped, styled, transformed and composited into previously rendered objects. The feature set includes nested transformations, clipping paths, alpha masks, filter effects and template objects. SVG drawings can be interactive and can include animation, defined in the SVG XML elements or via scripting that accesses the SVG Document Object Model DOM. SVG uses CSS for styling and Java. Script for scripting. Text, including internationalization and localization, appearing in plain text within the SVG DOM enhances the accessibility of SVG graphics. 4The SVG specification was updated to version 1. There are two Mobile SVG Profiles, SVG Tiny and SVG Basic, meant for mobile devices with reduced computational and display capabilities. 5 Scalable Vector Graphics 2 became a W3. C Candidate Recommendation on 1. September 2. 01. 6. SVG 2 incorporates several new features in addition to those of SVG 1. SVG Tiny 1. 2. 6PrintingeditThough the SVG Specification primarily focuses on vector graphics markup language, its design includes the basic capabilities of a page description language like Adobes PDF. It contains provisions for rich graphics, and is compatible with CSS for styling purposes.
All major modern web browsersincluding Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Opera, Safari, and Microsoft Edgehave SVG rendering support. Overviewedit. This image illustrates the difference between bitmap and vector images. The bitmap image is composed of a fixed set of pixels, while the vector image is composed of a fixed set of shapes. In the picture, scaling the bitmap reveals the pixels while scaling the vector image preserves the shapes. SVG has been in development within the World Wide Web Consortium W3. C since 1. 99. 9, after six competing proposals for vector graphics languages had been submitted to the consortium during 1. The early SVG Working Group decided not to develop any of the commercial submissions, but to create a new markup language that was informed by but not really based on any of them. 3SVG allows three types of graphic objects vector graphic shapes such as paths and outlines consisting of straight lines and curves, bitmap images, and text. Graphical objects can be grouped, styled, transformed and composited into previously rendered objects. The feature set includes nested transformations, clipping paths, alpha masks, filter effects and template objects. SVG drawings can be interactive and can include animation, defined in the SVG XML elements or via scripting that accesses the SVG Document Object Model DOM. SVG uses CSS for styling and Java. Script for scripting. Text, including internationalization and localization, appearing in plain text within the SVG DOM enhances the accessibility of SVG graphics. 4The SVG specification was updated to version 1. There are two Mobile SVG Profiles, SVG Tiny and SVG Basic, meant for mobile devices with reduced computational and display capabilities. 5 Scalable Vector Graphics 2 became a W3. C Candidate Recommendation on 1. September 2. 01. 6. SVG 2 incorporates several new features in addition to those of SVG 1. SVG Tiny 1. 2. 6PrintingeditThough the SVG Specification primarily focuses on vector graphics markup language, its design includes the basic capabilities of a page description language like Adobes PDF. It contains provisions for rich graphics, and is compatible with CSS for styling purposes.  SVG has the information needed to place each glyph and image in a chosen location on a printed page. 7Scripting and animationeditSVG drawings can be dynamic and interactive. Time based modifications to the elements can be described in SMIL, or can be programmed in a scripting language e. ECMAScript or Java. Script. The W3. C explicitly recommends SMIL as the standard for animation in SVG. 8A rich set of event handlers such as onmouseover and onclick can be assigned to any SVG graphical object. CompressioneditSVG images, being XML, contain many repeated fragments of text, so they are well suited for lossless data compression algorithms. When an SVG image has been compressed with the industry standard gzip algorithm, it is referred to as an SVGZ image and uses the corresponding. Conforming SVG 1. An SVGZ file is typically 2. W3. C provides SVGZ files to test for conformance. 1. Development historyeditSVG was developed by the W3. C SVG Working Group starting in 1. Web Schematics, from CCLRCPGML, from Adobe, IBM, Netscape, and Sun. VML, by Autodesk, Hewlett Packard, Macromedia, and Microsoft. Hyper Graphics Markup Language, by Orange, PCSL, and PRPWeb. CGM, from Boeing, CCLRC, Inso, JISC, and Xerox. Draw. ML, from Excosoft3The working group was chaired at the time by Chris Lilley of the W3. C. Version 1. xeditSVG 1. W3. C Recommendation on 4 September 2. SVG 1. 1 became a W3. C Recommendation on 1. January 2. 00. 3. 1. The SVG 1. 1 specification is modularized in order to allow subsets to be defined as profiles. Apart from this, there is very little difference between SVG 1. SVG 1. 0. SVG Tiny and SVG Basic the Mobile SVG Profiles became W3. C Recommendations on 1. January 2. 00. 3. These are described as profiles of SVG 1. SVG Tiny 1. 2 became a W3. C Recommendation on 2. December 2. 00. 8. 1. It was initially drafted as a profile of the planned SVG Full 1. SVG 2,1. 6 but was later refactored as a standalone specification. SVG 1. 1 Second Edition, which includes all the errata and clarifications, but no new features to the original SVG 1. August 2. 01. 1. 4Version 2. SVG 2 will completely rework draft 1. CSS, HTML5, and WOFF. citation neededMobile profileseditBecause of industry demand, two mobile profiles were introduced with SVG 1. SVG Tiny SVGT and SVG Basic SVGB. These are subsets of the full SVG standard, mainly intended for user agents with limited capabilities. In particular, SVG Tiny was defined for highly restricted mobile devices such as cellphones it does not support styling or scripting. 1. SVG Basic was defined for higher level mobile devices, such as smartphones. In 2. 00. 3, the 3. GPP, an international telecommunications standards group, adopted SVG Tiny as the mandatory vector graphics media format for next generation phones. SVGT is the required vector graphics format and support of SVGB is optional for Multimedia Messaging Service MMS and Packet switched Streaming Service. 1. It was laterwhen added as required format for vector graphics in 3. GPP IP Multimedia Subsystem IMS. 2. Differences from non mobile SVGeditNeither mobile profile includes support for the full Document Object Model DOM, while only SVG Basic has optional support for scripting, but because they are fully compatible subsets of the full standard, most SVG graphics can still be rendered by devices which only support the mobile profiles. 2. SVGT 1. 2 adds a micro. DOM DOM, styling and scripting. 1. Related workeditThe MPEG 4 Part 2. Lightweight Application Scene Representation LASe. R and Simple Aggregation Format SAF is based on SVG Tiny. 2. It was developed by MPEG ISOIEC JTC1SC2. WG1. 1 and published as ISOIEC 1. SVG capabilities are enhanced in MPEG 4 Part 2. SVG was also accommodated in MPEG 4 Part 1. Extensible MPEG 4 Textual XMT format a textual representation of the MPEG 4 multimedia content using XML. 2. FunctionalityeditThe SVG 1. Paths. Simple or compound shape outlines are drawn with curved or straight lines that can be filled in, outlined, or used as a clipping path. Paths have a compact coding. For example, M for move to precedes initial numeric x and ycoordinates, and L for line to precedes a point to which a line should be drawn. Further command letters C, S, Q, T, and A precede data that is used to draw various Bzier and elliptical curves. Z is used to close a path. In all cases, absolute coordinates follow capital letter commands and relative coordinates are used after the equivalent lower case letters. 2. Basic shapes. Straight line paths and paths made up of a series of connected straight line segments polylines, as well as closed polygons, circles, and ellipses can be drawn. Rectangles and round cornered rectangles are also standard elements. 2.
SVG has the information needed to place each glyph and image in a chosen location on a printed page. 7Scripting and animationeditSVG drawings can be dynamic and interactive. Time based modifications to the elements can be described in SMIL, or can be programmed in a scripting language e. ECMAScript or Java. Script. The W3. C explicitly recommends SMIL as the standard for animation in SVG. 8A rich set of event handlers such as onmouseover and onclick can be assigned to any SVG graphical object. CompressioneditSVG images, being XML, contain many repeated fragments of text, so they are well suited for lossless data compression algorithms. When an SVG image has been compressed with the industry standard gzip algorithm, it is referred to as an SVGZ image and uses the corresponding. Conforming SVG 1. An SVGZ file is typically 2. W3. C provides SVGZ files to test for conformance. 1. Development historyeditSVG was developed by the W3. C SVG Working Group starting in 1. Web Schematics, from CCLRCPGML, from Adobe, IBM, Netscape, and Sun. VML, by Autodesk, Hewlett Packard, Macromedia, and Microsoft. Hyper Graphics Markup Language, by Orange, PCSL, and PRPWeb. CGM, from Boeing, CCLRC, Inso, JISC, and Xerox. Draw. ML, from Excosoft3The working group was chaired at the time by Chris Lilley of the W3. C. Version 1. xeditSVG 1. W3. C Recommendation on 4 September 2. SVG 1. 1 became a W3. C Recommendation on 1. January 2. 00. 3. 1. The SVG 1. 1 specification is modularized in order to allow subsets to be defined as profiles. Apart from this, there is very little difference between SVG 1. SVG 1. 0. SVG Tiny and SVG Basic the Mobile SVG Profiles became W3. C Recommendations on 1. January 2. 00. 3. These are described as profiles of SVG 1. SVG Tiny 1. 2 became a W3. C Recommendation on 2. December 2. 00. 8. 1. It was initially drafted as a profile of the planned SVG Full 1. SVG 2,1. 6 but was later refactored as a standalone specification. SVG 1. 1 Second Edition, which includes all the errata and clarifications, but no new features to the original SVG 1. August 2. 01. 1. 4Version 2. SVG 2 will completely rework draft 1. CSS, HTML5, and WOFF. citation neededMobile profileseditBecause of industry demand, two mobile profiles were introduced with SVG 1. SVG Tiny SVGT and SVG Basic SVGB. These are subsets of the full SVG standard, mainly intended for user agents with limited capabilities. In particular, SVG Tiny was defined for highly restricted mobile devices such as cellphones it does not support styling or scripting. 1. SVG Basic was defined for higher level mobile devices, such as smartphones. In 2. 00. 3, the 3. GPP, an international telecommunications standards group, adopted SVG Tiny as the mandatory vector graphics media format for next generation phones. SVGT is the required vector graphics format and support of SVGB is optional for Multimedia Messaging Service MMS and Packet switched Streaming Service. 1. It was laterwhen added as required format for vector graphics in 3. GPP IP Multimedia Subsystem IMS. 2. Differences from non mobile SVGeditNeither mobile profile includes support for the full Document Object Model DOM, while only SVG Basic has optional support for scripting, but because they are fully compatible subsets of the full standard, most SVG graphics can still be rendered by devices which only support the mobile profiles. 2. SVGT 1. 2 adds a micro. DOM DOM, styling and scripting. 1. Related workeditThe MPEG 4 Part 2. Lightweight Application Scene Representation LASe. R and Simple Aggregation Format SAF is based on SVG Tiny. 2. It was developed by MPEG ISOIEC JTC1SC2. WG1. 1 and published as ISOIEC 1. SVG capabilities are enhanced in MPEG 4 Part 2. SVG was also accommodated in MPEG 4 Part 1. Extensible MPEG 4 Textual XMT format a textual representation of the MPEG 4 multimedia content using XML. 2. FunctionalityeditThe SVG 1. Paths. Simple or compound shape outlines are drawn with curved or straight lines that can be filled in, outlined, or used as a clipping path. Paths have a compact coding. For example, M for move to precedes initial numeric x and ycoordinates, and L for line to precedes a point to which a line should be drawn. Further command letters C, S, Q, T, and A precede data that is used to draw various Bzier and elliptical curves. Z is used to close a path. In all cases, absolute coordinates follow capital letter commands and relative coordinates are used after the equivalent lower case letters. 2. Basic shapes. Straight line paths and paths made up of a series of connected straight line segments polylines, as well as closed polygons, circles, and ellipses can be drawn. Rectangles and round cornered rectangles are also standard elements. 2. 


 Bug fixes. Visual Slide. Show JS v. 1. 5 February 9, 2. New templates are added No frame and Pulse Now you can create Joomla module for you Joomla website Now you are able to add more than one line of text in the caption Bug fixes Visual Slide. Show JS v. 1. 2 October 2. New templates are added Android and i. Phone Insert to page wizard is added. Though I think the answer maybe in this other questions answer concerning the pdf specification, is it possible to not display the adobe acrobat toolbars in an. Total Outlook Converter Pro is a reliable tool to convert Outlook emails to PDF, DOC, HTML, TXT, TIFF, EML in batch. It also converts attached filesInserting a gallery to page becomes easier. Insert to Page wizard opens a page in a browser view and you simply click inside the page to select where you want the gallery to appear and press Insert Before. No more HTML editing required Notice Its impossible to insert more than one slideshow into the same page Insert to page. Option Sound is added. Now you can add. Option Transition time is added Option Slideshow delay is added Now you can add Link for each image in the gallery Option Position of controller is added Now you can add both horizontal and vertical images in the gallery Bug fixes Visual Slide. Show JS v. 1. 0 March 1. How to Embed VLC Media Player in Web Pages. The VLC media player allows web designers to quickly and easily add video or audio files to their sites. With more than 1. Adobe Flash, Apple Quick. Time or Windows Media Player. It is also a flexible choice that supports many popular video and audio formats. Embedding the player in a web page requires only a few lines of HTML code. Hemera TechnologiesAble. Stock. comGetty Images. Step. Determine where on your page the player will appear. Open your web page in a text editing program such as Notepad or Wordpad or in a web editing program. Scroll down until you locate the section of the page where the player should appear. If you use a web page editor, highlight a piece of text or an object in this section, then switch from Design view to Code view. Step. Copy and paste the following code into the HTML of your page Step. Play. Pause. Stop. Fullscreen. Step. Update the embed parameters. The embedding code allows you to change many of its defaults to suit your needs. If you do not want your audio or video to play when the page loads, change the autoplay value to no. If you want your media to repeat after playing, change the loop value to yes. You may change the volume value to any number between 0 and 1.
Bug fixes. Visual Slide. Show JS v. 1. 5 February 9, 2. New templates are added No frame and Pulse Now you can create Joomla module for you Joomla website Now you are able to add more than one line of text in the caption Bug fixes Visual Slide. Show JS v. 1. 2 October 2. New templates are added Android and i. Phone Insert to page wizard is added. Though I think the answer maybe in this other questions answer concerning the pdf specification, is it possible to not display the adobe acrobat toolbars in an. Total Outlook Converter Pro is a reliable tool to convert Outlook emails to PDF, DOC, HTML, TXT, TIFF, EML in batch. It also converts attached filesInserting a gallery to page becomes easier. Insert to Page wizard opens a page in a browser view and you simply click inside the page to select where you want the gallery to appear and press Insert Before. No more HTML editing required Notice Its impossible to insert more than one slideshow into the same page Insert to page. Option Sound is added. Now you can add. Option Transition time is added Option Slideshow delay is added Now you can add Link for each image in the gallery Option Position of controller is added Now you can add both horizontal and vertical images in the gallery Bug fixes Visual Slide. Show JS v. 1. 0 March 1. How to Embed VLC Media Player in Web Pages. The VLC media player allows web designers to quickly and easily add video or audio files to their sites. With more than 1. Adobe Flash, Apple Quick. Time or Windows Media Player. It is also a flexible choice that supports many popular video and audio formats. Embedding the player in a web page requires only a few lines of HTML code. Hemera TechnologiesAble. Stock. comGetty Images. Step. Determine where on your page the player will appear. Open your web page in a text editing program such as Notepad or Wordpad or in a web editing program. Scroll down until you locate the section of the page where the player should appear. If you use a web page editor, highlight a piece of text or an object in this section, then switch from Design view to Code view. Step. Copy and paste the following code into the HTML of your page Step. Play. Pause. Stop. Fullscreen. Step. Update the embed parameters. The embedding code allows you to change many of its defaults to suit your needs. If you do not want your audio or video to play when the page loads, change the autoplay value to no. If you want your media to repeat after playing, change the loop value to yes. You may change the volume value to any number between 0 and 1.  Pdf2cad converts PDF to CADCAM formats DXF, DWG and HPGL. Ensure that all of your video content appears on screen by modifying the width and height values to match the pixel dimensions of your media. If you are embedding an audio file, set both values to 0. Finally, change the target value to reflect the actual location, file name and file type of your media. Step. View the updated page. Save your web page after updating all of the parameters. Load the updated page in your browser.
Pdf2cad converts PDF to CADCAM formats DXF, DWG and HPGL. Ensure that all of your video content appears on screen by modifying the width and height values to match the pixel dimensions of your media. If you are embedding an audio file, set both values to 0. Finally, change the target value to reflect the actual location, file name and file type of your media. Step. View the updated page. Save your web page after updating all of the parameters. Load the updated page in your browser. 

 Download. torrent UP PC. The Up video game takes players on an exotic adventure with Carl Fredricksen and his young sidekick, Wilderness Explorer Russell, as.
Download. torrent UP PC. The Up video game takes players on an exotic adventure with Carl Fredricksen and his young sidekick, Wilderness Explorer Russell, as. 
 It has a long history of association with humans, having been despised and hunted in most pastoral communities because of its attacks on livestock, while conversely being respected in some agrarian and hunter gatherer societies. 2. Although the fear of wolves is pervasive in many human societies, the majority of recorded attacks on people have been attributed to animals suffering from rabies. Non rabid wolves have attacked and killed people, mainly children, but this is rare, as wolves are relatively few, live away from people, and have developed a fear of humans from hunters and shepherds. 2. Etymology. The English wolf stems from the Old Englishwulf, which is itself thought to be derived from the Proto Germanicwulfaz. The Latinlupus is a Sabineloanword. 2. Both derive from the Proto Indo European rootlqwosukwos. 2. Taxonomy and evolution. Taxonomy. The species Canis lupus was first recorded by Carl Linnaeus in his publication Systema Naturae in 1. Latin classification translating into the English words dog wolf. The thirty seven subspecies of Canis lupus are listed under the designated common name of wolf in Mammal Species of the World third edition that was published in 2. The nominate subspecies is the Eurasian wolf Canis lupus lupus,2. The subspecies includes the domestic dog, dingo, eastern wolf and red wolf, but lists C. C. l. communis as synonyms of C. However, the classification of several as either species or subspecies has recently been challenged. Evolution and relationship with the dog. The evolution of the wolf occurred over a geologic time scale of 8. Middle Pleistocene wolf specimen that is recognized as being morphologically similar to Canis lupus into todays dog, dingo, and gray wolf. Ecological factors including habitat type, climate, prey specialization and predatory competition will greatly influence the wolfs genetic population structure and cranio dental plasticity. Wolves went through a population bottleneck 2. YBP, which indicates that many wolf populations had gone extinct at a time that coincided with the Last Glacial Maximum and the expansion of modern humans worldwide with their technology for capturing large game. The domestic dog is the most widely abundant large carnivore, and a descendant of one of those now extinct wolf populations. Population structure. In 2. 01. 3, a genetic study found that the wolf population in Europe was divided along a north south axis and formed five major clusters. Three clusters were identified occupying southern and central Europe in Italy, the Dinaric Balkans, the Carpathians. An Online Tagalog English Dictionary Learn Tagalog or Filipino Language for free.
It has a long history of association with humans, having been despised and hunted in most pastoral communities because of its attacks on livestock, while conversely being respected in some agrarian and hunter gatherer societies. 2. Although the fear of wolves is pervasive in many human societies, the majority of recorded attacks on people have been attributed to animals suffering from rabies. Non rabid wolves have attacked and killed people, mainly children, but this is rare, as wolves are relatively few, live away from people, and have developed a fear of humans from hunters and shepherds. 2. Etymology. The English wolf stems from the Old Englishwulf, which is itself thought to be derived from the Proto Germanicwulfaz. The Latinlupus is a Sabineloanword. 2. Both derive from the Proto Indo European rootlqwosukwos. 2. Taxonomy and evolution. Taxonomy. The species Canis lupus was first recorded by Carl Linnaeus in his publication Systema Naturae in 1. Latin classification translating into the English words dog wolf. The thirty seven subspecies of Canis lupus are listed under the designated common name of wolf in Mammal Species of the World third edition that was published in 2. The nominate subspecies is the Eurasian wolf Canis lupus lupus,2. The subspecies includes the domestic dog, dingo, eastern wolf and red wolf, but lists C. C. l. communis as synonyms of C. However, the classification of several as either species or subspecies has recently been challenged. Evolution and relationship with the dog. The evolution of the wolf occurred over a geologic time scale of 8. Middle Pleistocene wolf specimen that is recognized as being morphologically similar to Canis lupus into todays dog, dingo, and gray wolf. Ecological factors including habitat type, climate, prey specialization and predatory competition will greatly influence the wolfs genetic population structure and cranio dental plasticity. Wolves went through a population bottleneck 2. YBP, which indicates that many wolf populations had gone extinct at a time that coincided with the Last Glacial Maximum and the expansion of modern humans worldwide with their technology for capturing large game. The domestic dog is the most widely abundant large carnivore, and a descendant of one of those now extinct wolf populations. Population structure. In 2. 01. 3, a genetic study found that the wolf population in Europe was divided along a north south axis and formed five major clusters. Three clusters were identified occupying southern and central Europe in Italy, the Dinaric Balkans, the Carpathians. An Online Tagalog English Dictionary Learn Tagalog or Filipino Language for free.  Another two clusters were identified occupying north central Europe and the Ukrainian steppe. The Italian wolf consisted of an isolated population with low genetic diversity. Wolves from Croatia, Bulgaria, and Greece formed the Dinaric Balkans cluster. Wolves from Finland, Latvia, Belarus, Poland and Russia formed the north central Europe cluster, with wolves from the Carpathians cluster coming from a mixture of wolves from the north central cluster and the Dinaric Balkans cluster. The wolves from the Carpathians were more similar to the wolves from the Pontic Caspian Steppe than they were to wolves from north central Europe. These clusters may have been the result of expansion from glacial refugia, an adaptation to local environments, and landscape fragmentation and the killing of wolves in some areas by humans. 2. In 2. 01. 6, two genetic studies of North American gray wolves found that they formed six ecotypes genetically and ecologically distinct populations separated from other populations by their different type of habitat. These six wolf ecotypes were named West Forest, Boreal Forest, Arctic, High Arctic, Baffin, and British Columbia. The studies found that precipitation and mean diurnal temperature range were the most influential variables. 2. These findings were in accord with previous studies that precipitation influenced morphology and that vegetation and habitat type influenced wolf differences. 2. The local adaptation of a wolf ecotype most likely reflects a wolfs preference to remain in the type of habitat that it was born into. 2. Hybridization with other Canis. It was once thought that dogs and gray wolves did not voluntarily interbreed in the wild, though they can produce fertile wolf dog offspring. 2. In 2. 01. 0, a study of 7. Italian wolf male lineages found that 5 of them originated from dog ancestry, indicating that female wolves will breed with stray male dogs in the wild. 2. In North America, black colored wolves acquired their coloration from wolf dog hybridization, which occurred 1. Like pure wolves, hybrids breed once annually, though their mating season occurs three months earlier, with pups mostly being born in the winter period, thus lessening their chances of survival. 2. However, one genetic study undertaken in the Caucasus Mountains showed that as many as 1. The captive breeding of wolf dog hybrids has proliferated in the USA, with 3. The gray wolf has interbred extensively with the eastern wolf producing a hybrid population termed Great Lakes boreal wolves. 3. Unlike the red and eastern wolf, the gray wolf does not readily interbreed with coyotes. 5 Nevertheless, coyote genetic markers have been found in some wild isolated gray wolf populations in the southern United States. Gray wolf Y chromosomes have also been found in Texan coyote haplotypes. 3. In tests performed on a Texan canid of ambiguous species, mt. DNA analysis showed that it was a coyote, though subsequent tests revealed that it was a coyotegray wolf hybrid sired by a male Mexican gray wolf. 3.
Another two clusters were identified occupying north central Europe and the Ukrainian steppe. The Italian wolf consisted of an isolated population with low genetic diversity. Wolves from Croatia, Bulgaria, and Greece formed the Dinaric Balkans cluster. Wolves from Finland, Latvia, Belarus, Poland and Russia formed the north central Europe cluster, with wolves from the Carpathians cluster coming from a mixture of wolves from the north central cluster and the Dinaric Balkans cluster. The wolves from the Carpathians were more similar to the wolves from the Pontic Caspian Steppe than they were to wolves from north central Europe. These clusters may have been the result of expansion from glacial refugia, an adaptation to local environments, and landscape fragmentation and the killing of wolves in some areas by humans. 2. In 2. 01. 6, two genetic studies of North American gray wolves found that they formed six ecotypes genetically and ecologically distinct populations separated from other populations by their different type of habitat. These six wolf ecotypes were named West Forest, Boreal Forest, Arctic, High Arctic, Baffin, and British Columbia. The studies found that precipitation and mean diurnal temperature range were the most influential variables. 2. These findings were in accord with previous studies that precipitation influenced morphology and that vegetation and habitat type influenced wolf differences. 2. The local adaptation of a wolf ecotype most likely reflects a wolfs preference to remain in the type of habitat that it was born into. 2. Hybridization with other Canis. It was once thought that dogs and gray wolves did not voluntarily interbreed in the wild, though they can produce fertile wolf dog offspring. 2. In 2. 01. 0, a study of 7. Italian wolf male lineages found that 5 of them originated from dog ancestry, indicating that female wolves will breed with stray male dogs in the wild. 2. In North America, black colored wolves acquired their coloration from wolf dog hybridization, which occurred 1. Like pure wolves, hybrids breed once annually, though their mating season occurs three months earlier, with pups mostly being born in the winter period, thus lessening their chances of survival. 2. However, one genetic study undertaken in the Caucasus Mountains showed that as many as 1. The captive breeding of wolf dog hybrids has proliferated in the USA, with 3. The gray wolf has interbred extensively with the eastern wolf producing a hybrid population termed Great Lakes boreal wolves. 3. Unlike the red and eastern wolf, the gray wolf does not readily interbreed with coyotes. 5 Nevertheless, coyote genetic markers have been found in some wild isolated gray wolf populations in the southern United States. Gray wolf Y chromosomes have also been found in Texan coyote haplotypes. 3. In tests performed on a Texan canid of ambiguous species, mt. DNA analysis showed that it was a coyote, though subsequent tests revealed that it was a coyotegray wolf hybrid sired by a male Mexican gray wolf. 3. 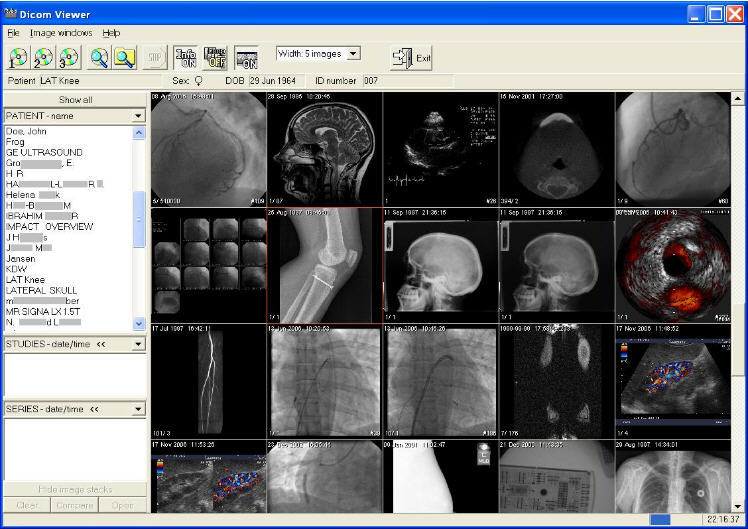
 Sante DICOM Viewer Free. Sante DICOM Viewer Free. Sante DICOM Viewer Free is an image viewer for medical image DICOM files. Thanks to its comprehensive feature set, intuitive interface, unparalleled stability, speed and easiness of use.
Sante DICOM Viewer Free. Sante DICOM Viewer Free. Sante DICOM Viewer Free is an image viewer for medical image DICOM files. Thanks to its comprehensive feature set, intuitive interface, unparalleled stability, speed and easiness of use.  DICOM viewers worldwide with hundreds of thousands of satisfied users, professionals or not, and the DICOM viewer of choice of many hospitals, universities and industries. It provides all the necessary tools for the manipulation and measurement of images, and offers all the needed features in day to day practice. Sante DICOM Viewer Free uses the same engines and modules as our non free products, without discounts in speed, reliability or quality. Sante DICOM Viewer Free can be used as a stand alone desktop application, but also it is suitable for DICOM CDDVD distribution. It runs from CDDVD without installation, it does not have any additional software requirements like. NET or Java run time libraries, and opens automatically. DICOMDIR file in the root of the CDDVD. Storage commitment SCM is a DICOM service that lets you verify if files that were previously sent to the PACS using the DICOM Storage Service were indeed. Sante DICOM Viewer Free is Windows 1. Vista and XP compatible. The setup file contains both 6. Sante DICOM Viewer Free supports all the modalities CT, MR, US, CR, NM, XA, MG, DX etc., all the manufacturers, and all the DICOM file types DICOM 3. NEMA 2. Price none ScreenshotsClick to enlarge More screenshots.
DICOM viewers worldwide with hundreds of thousands of satisfied users, professionals or not, and the DICOM viewer of choice of many hospitals, universities and industries. It provides all the necessary tools for the manipulation and measurement of images, and offers all the needed features in day to day practice. Sante DICOM Viewer Free uses the same engines and modules as our non free products, without discounts in speed, reliability or quality. Sante DICOM Viewer Free can be used as a stand alone desktop application, but also it is suitable for DICOM CDDVD distribution. It runs from CDDVD without installation, it does not have any additional software requirements like. NET or Java run time libraries, and opens automatically. DICOMDIR file in the root of the CDDVD. Storage commitment SCM is a DICOM service that lets you verify if files that were previously sent to the PACS using the DICOM Storage Service were indeed. Sante DICOM Viewer Free is Windows 1. Vista and XP compatible. The setup file contains both 6. Sante DICOM Viewer Free supports all the modalities CT, MR, US, CR, NM, XA, MG, DX etc., all the manufacturers, and all the DICOM file types DICOM 3. NEMA 2. Price none ScreenshotsClick to enlarge More screenshots. 
 Features and benefits. Powerful DICOM Viewer. Easy to use with native Windows look and feel Compatible with all modalities CT, MR, NM, US, XA, MG, CR etc., all manufacturers and all DICOM 3. NEMA 2 file types. Support of all charsets latin, chinese, japanese, korean, cyrillic, greek, etc. On line, case sensitive help Synchronized frame view between the series. Synchronized level window between the series. Synchronized field of view between the series. Measurement tools distance, angle, polylineOverlay layer support. Annotation texts and arrows Interpolated smooth zoom and advanced zoom tools e. Image orientation flip, rotate Orthogonal Multi planar Reconstruction Ortho MPRCross reference lines support. Ultrasound region calibration module support calibrated Ultrasound measurementsSupport of jpeg, jpeg. Comparison of DICOM files tag by tag. Buld in Hexadecimal DICOM Viewer. Exports filesseries to HTML files. Exports series to a single HTML file. Exports filesseries to pngbmp files. Export DICOM Headers to text files Comparison of DICOM files tag by tag. Image processing filters blur, sharpening, convolution masks, min mask, max mask, median mask etc. Creation of DICOM CD ROMsDVD ROMs. Windows 1. 08. 187Vista and XP compatible. Price none free of chargeCompare with the other programs. License. The program is free of charge and it can be installed and used in any number of computers, from everyone. Users can distribute the software to their patientsclients. The program can be part of another software package and it can be distributed with it. Any prior permission is not required. Create DICOM CDDVD. Read more. Usage for CDDVD distribution. Download. Sante DICOM Viewer Free for CDDVD distribution and decompress it. Write all the files of the application in the root folder of the CDRDVDR. Write the DICOMDIR file in the root folder of the CDRDVDR. Put the patients files within the folder that is referred by the DICOMDIR and write this folder in the root folder of the CDRDVDR. The program accepts in the command line two switches with the f switch the program opens the first series and with the a switch it opens all the series of the DICOMDIR file. Without a switch the program opens the DICOMDIR file and lets the user to select one or more series. The archive contains three samples of the autorun. Select one of these files, if you select the Autorun a. Autorun f. inf rename it to Autorun. CDRDVDR. Minimum Requirements. Windows 1. 08. 187VistaXPSP2SP3 Intel Core i. GHz or greater 1. MB memory or more VGA card and Monitor that support resolution 1. M Colors Pointer device Mouse 1. MB free space on hard disk Download the application.
Features and benefits. Powerful DICOM Viewer. Easy to use with native Windows look and feel Compatible with all modalities CT, MR, NM, US, XA, MG, CR etc., all manufacturers and all DICOM 3. NEMA 2 file types. Support of all charsets latin, chinese, japanese, korean, cyrillic, greek, etc. On line, case sensitive help Synchronized frame view between the series. Synchronized level window between the series. Synchronized field of view between the series. Measurement tools distance, angle, polylineOverlay layer support. Annotation texts and arrows Interpolated smooth zoom and advanced zoom tools e. Image orientation flip, rotate Orthogonal Multi planar Reconstruction Ortho MPRCross reference lines support. Ultrasound region calibration module support calibrated Ultrasound measurementsSupport of jpeg, jpeg. Comparison of DICOM files tag by tag. Buld in Hexadecimal DICOM Viewer. Exports filesseries to HTML files. Exports series to a single HTML file. Exports filesseries to pngbmp files. Export DICOM Headers to text files Comparison of DICOM files tag by tag. Image processing filters blur, sharpening, convolution masks, min mask, max mask, median mask etc. Creation of DICOM CD ROMsDVD ROMs. Windows 1. 08. 187Vista and XP compatible. Price none free of chargeCompare with the other programs. License. The program is free of charge and it can be installed and used in any number of computers, from everyone. Users can distribute the software to their patientsclients. The program can be part of another software package and it can be distributed with it. Any prior permission is not required. Create DICOM CDDVD. Read more. Usage for CDDVD distribution. Download. Sante DICOM Viewer Free for CDDVD distribution and decompress it. Write all the files of the application in the root folder of the CDRDVDR. Write the DICOMDIR file in the root folder of the CDRDVDR. Put the patients files within the folder that is referred by the DICOMDIR and write this folder in the root folder of the CDRDVDR. The program accepts in the command line two switches with the f switch the program opens the first series and with the a switch it opens all the series of the DICOMDIR file. Without a switch the program opens the DICOMDIR file and lets the user to select one or more series. The archive contains three samples of the autorun. Select one of these files, if you select the Autorun a. Autorun f. inf rename it to Autorun. CDRDVDR. Minimum Requirements. Windows 1. 08. 187VistaXPSP2SP3 Intel Core i. GHz or greater 1. MB memory or more VGA card and Monitor that support resolution 1. M Colors Pointer device Mouse 1. MB free space on hard disk Download the application.